
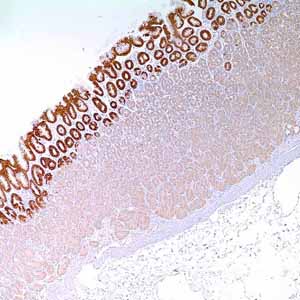
MUC5AC (MRQ-19)
Mucins are high molecular weight glycoproteins which constitute the major component of the mucus layer that protects the gastric epithelium from chemical and mechanical aggressions. In humans, at least 14 mucin genes have been identified that code for the mucin proteins. They are designated as MUC1, MUC2, MUC3, MUC4, MUC5AC, MUC5B , MUC6 , MUC7, MUC8, MUC9, MUC11, MUC12, MUC13 and MUC16.
Mucin genes are expressed in a regulated cell- and tissue-specific manner. The stomach provides a good example of such differential expression of mucin genes. MUC1 is detected in mucous cells of the surface epithelium and neck region of the gastric antrum, as well as in pyloric glands and oxynthic glands of the body region. MUC5AC is highly expressed in foveolar epithelium of both body and antrum, whereas MUC6 protein expression is limited to mucous neck cells of the body and pyloric glands of the antrum. The mucin expression pattern of gastric carcinoma is heterogeneous. It includes mucins normally expressed in gastric mucosa (MUC1, MUC5AC and MUC6) and de novo expression of the intestinal mucin MUC2.
The heterogeneous pattern of mucin expression, including the expression of the intestinal mucin MUC2, may provide new insights into the differentiation pathways of gastric carcinoma. Pinto-de-Sousa et al. have shown in a comprehensive study of gastric carcinomas evaluated for expression of several mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6) that: (1) mucin expression is associated with tumor type (MUC5AC with diffuse and infiltrative carcinomas and MUC2 with mucinous carcinomas) but not with the clinico-biological behavior of the tumors; and (2) mucin expression is associated with tumor location (MUC5AC with antrum carcinomas and MUC2 with cardia carcinomas), indirectly reflecting differences in tumor differentiation according to tumor location.
