
Insulin
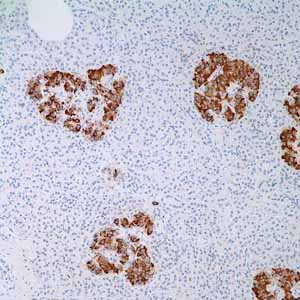
Insulin is a 51-amino acid polypeptide composed of A and B chains connected through the C-peptide. Insulin is one of the major regulatory hormones of intermediate metabolism throughout the body. The biological actions of this hormone involve integration of carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism. Insulin enhances membrane transport of glucose, amino acids, and certain ions. It also promotes glycogen storage, formation of triglycerides, and synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids. Immunohistochemical investigations have localized insulin in the beta cells of pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Defficiency of insulin results in diabetes mellitus, one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the general population. Insulin is also present in tumors of beta cell origin such as insulinoma. Anti-insulin staining in the cytoplasm of tumors is the most reliable indication of functional insulinomas.
