
Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CA IX) (EP161)
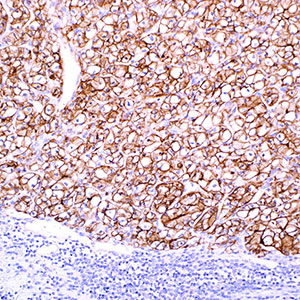
Carbonic anhydrases are a family of zinc containing metalloproteins that catalyze the reversible hydration of CO2. Among these, carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) is anchored to the cell membrane and is expressed in the human gastrointestinal tract, chiefly in the stomach and gall bladder1. It is interesting to note that CA IX is overexpressed in epithelial malignancies of the uterus, cervix, lung, breast, and kidney; none of the associated normal tissues express this isozyme.1-4 CA IX is said to maintain the extracellular acidic pH, thus promoting cell growth in these tumors.5 Preliminary data suggest consistent immunoreactivity for anti-CA IX in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with demonstrated sensitivity of 85% to 100%.2 Anti-CA IX, together with antibodies against PAX-2, Ksp-cadherin, and CD117, contributes to a robust panel that can be used to help make this distinction. Strong diffuse-to-multifocal immunostaining for anti-CA IX is observed in the large majority of urothelial carcinomas as opposed to the extremely weak and focal immunoreactivity seen in collecting duct carcinoma (CDC). Anti-CA IX can thus aid in distinguishing between urothelial carcinoma and CDC.6
